Omega-3s: maybe you’ve heard of them, or maybe you’ve never even thought about these essential fats. In this guide, we’re answering all of your omega-3 questions and talking about why omega-3s for women are so crucial.

Why are omega-3 fatty acids important?
Omega-3s are important for women to maintain their health through all stages of the lifecycle, but especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of essential fatty acids, which means they are an essential part of our diet because our bodies cannot make them. In other words, we must get them from food (or supplements) on a regular basis to be healthy.
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for brain and eye health, increase the likelihood of conception, healthy pregnancy, and are associated with lower risk of cardiovascular disease, PMS cramps, endometriosis, and reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids have even been linked to improved mood and prevention of depression and dementia.
Where do you find omega-3s?
There are three important types of omega-3s: alpha-linoleic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found in plant foods, specifically flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts.
EPA and DHA are technically not considered essential because the body can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, however it is unclear how reliable and consistent this conversion is. EPA and DHA are found in animal foods like fatty fish. Because fish is so often contaminated with toxins like mercury, I currently do not recommend relying on fish as a daily DHA/EPA source. An algae-based supplement will provide everything you need without the added toxins.
How much do you need?
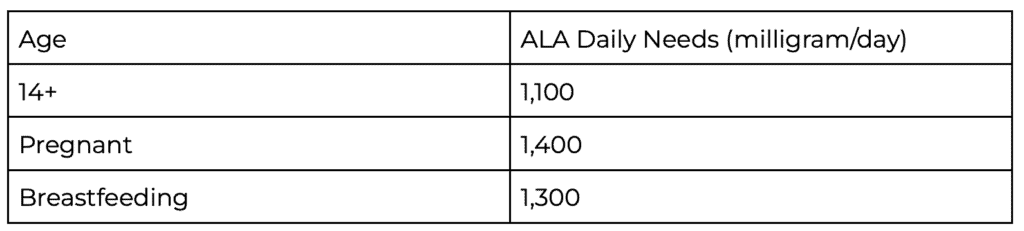
It is very important for women to eat sources of ALA omega-3 fatty acids everyday. The Institute of Medicine recommends adult women get 1,100 milligrams/day, and increase to 1,400 milligrams when pregnant and 1,300 milligrams per day when breastfeeding.
Because of the uncertainty about conversion and the importance of these fatty acids for women’s health, I usually recommend an occasional (2-3 times per week) 200-300mg algae-based DHA/EPA supplement for women and a daily 300mg algae-based DHA/EPA supplement when pregnant or breastfeeding in addition to eating ALA-rich foods everyday.
ALA Needs For Women
Tips For Meeting Omega-3 Needs
- Eat at least one serving of an omega-3 rich food every day to meet ALA needs:
- 1 tbsp. ground flaxseeds or chia seeds
- 2 tbsp. hempseeds
- About 10 walnut halves
- Consider taking 200-300mg of an algae-based DHA/EPA supplement a few times per week
- If pregnant or breastfeeding, take a 300mg algae-based DHA/EPA supplement daily
Common Questions About Omega-3s for Women
Should you eat fish or take fish oil supplements?
Some fatty fish contain EPA and DHA, which is why fish oil is a popular supplement. However, fish get their EPA and DHA from seaweed, so I recommend going straight to the source and avoiding the mercury and other contaminants often found in fish and fish oils. Algae-based supplements are also more sustainable from an environmental perspective. In other words, you do not need fish or fish oil to meet your needs. If you do choose to eat fish, check the Monetary Bay Aquarium Seafood Watch tool to find the lowest mercury seafood options. If you are pregnant, it is especially critical to only choose low-mercury fish varieties.
Do you need to worry about omega-6 fatty acids?
Omega-6s are another type of essential fatty acid found abundantly in many nuts and seeds and in soybean, sunflower, safflower, and corn oils. Most people easily meet omega-6 needs. Omega-6s have been the source of controversy, with conflicting evidence that suggests omega-6 is pro-inflammatory as well as that it is health protective. But the American Heart Association settled the controversy in their 2009 review which concluded that omega-6s seem to be beneficial or neutral to health. So, there is no need to worry about your omega-6 intake, and it’s best to focus on making sure you get enough omega-3s.


